
OTC Drugs
What are OTC drugs;
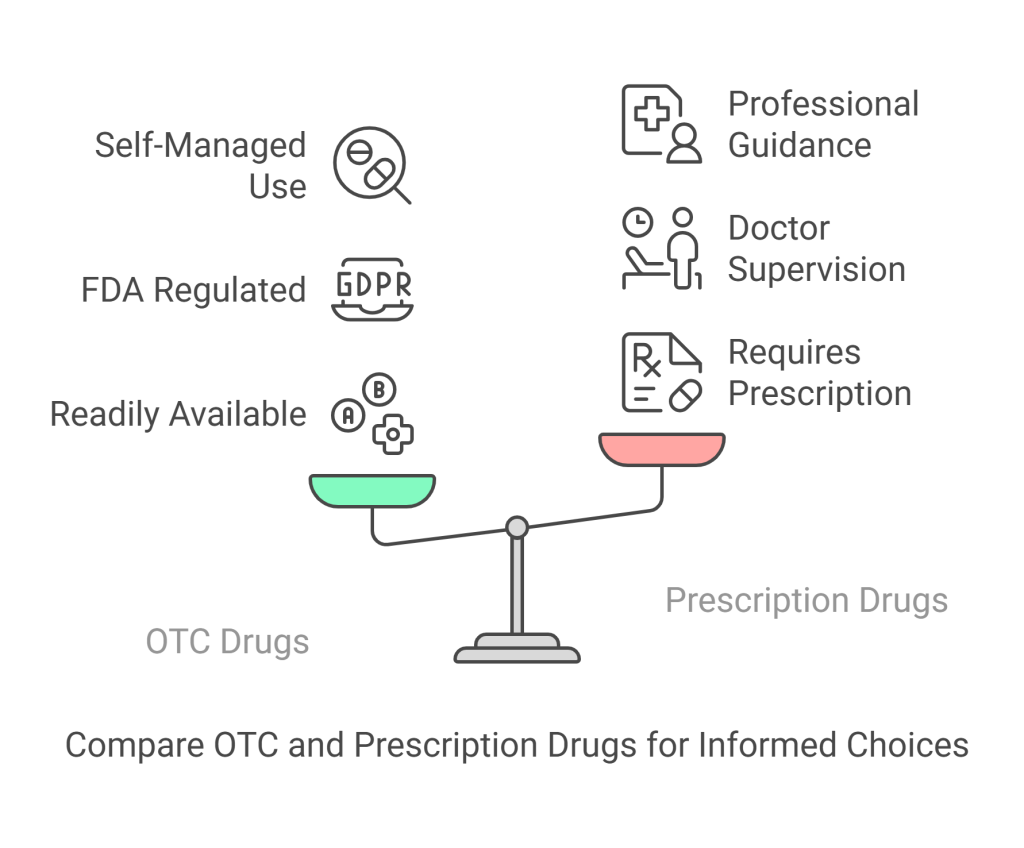
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are medications that can be purchased without a prescription and are widely used to treat minor health issues such as headaches, colds, and allergies. These drugs are regulated by government agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, ensuring they are safe and effective when used as directed. OTC drugs are readily available in pharmacies, supermarkets, and convenience stores, making them an accessible option for managing common ailments. Examples include pain relievers like ibuprofen and acetaminophen, antihistamines, and cough suppressants.
While OTC drugs are generally safe, improper use can lead to adverse effects or interactions with other medications. Consumers must carefully follow the instructions on the packaging and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen. Certain groups, such as children, pregnant women, and individuals with chronic illnesses, may need extra caution when using OTC drugs. Responsible use of these medications helps maintain their safety and effectiveness in addressing everyday health concerns.
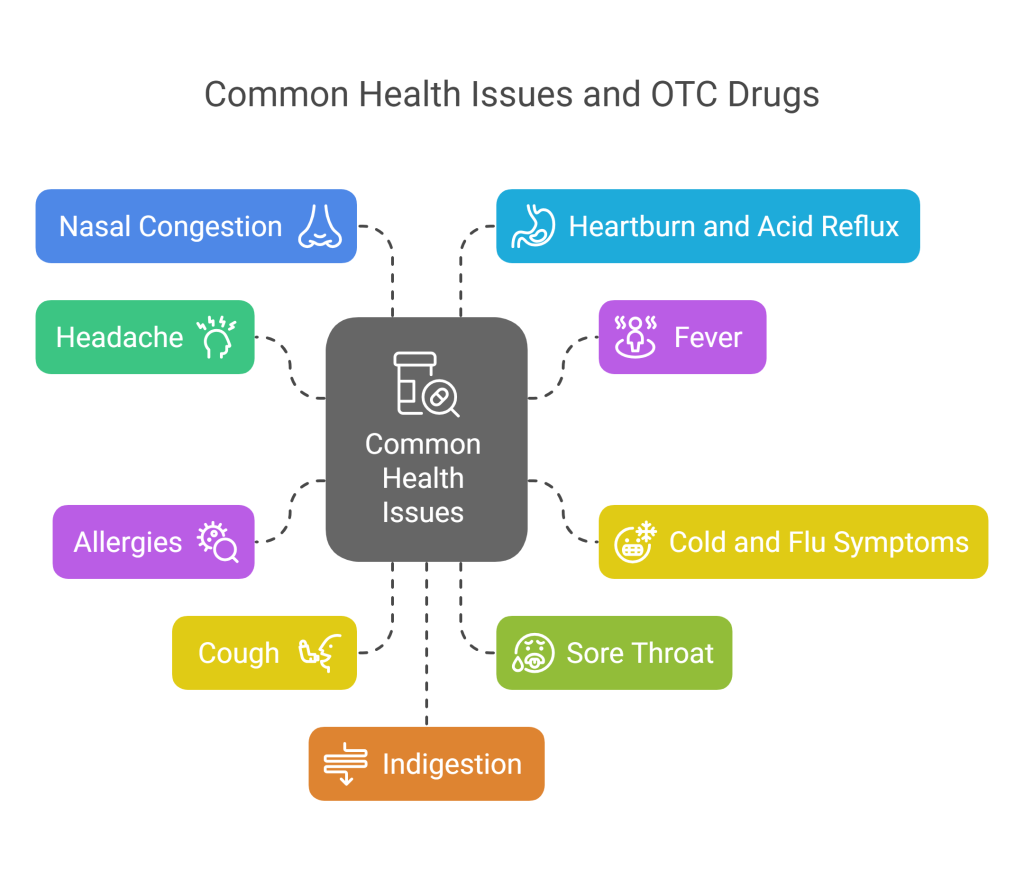
Common Health issues for OTC Drugs
Mentioned below are 20 of the most common health issues for which OTC drugs are frequently used:
- Headache
- Fever
- Cold and flu symptoms
- Allergies
- Cough
- Sore throat
- Nasal congestion
- Heartburn and acid reflux
- Indigestion
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Motion sickness
- Minor pain (e.g., muscle aches, menstrual cramps)
- Skin rashes or irritation
- Itchy skin or hives
- Athlete’s foot or fungal infections
- Dry eyes or eye irritation
- Minor cuts and scrapes
- Insomnia or difficulty sleeping
Common OTC Drugs
Here are 20 commonly used OTC drugs:
- Acetaminophen – Pain reliever and fever reducer
- Ibuprofen – Pain reliever, anti-inflammatory, and fever reducer
- Aspirin – Pain reliever, anti-inflammatory, and fever reducer
- Naproxen – Pain reliever and anti-inflammatory
- Diphenhydramine – Antihistamine for allergies and sleep aid
- Loratadine – Antihistamine for allergies
- Cetirizine – Antihistamine for allergies
- Fexofenadine – Antihistamine for allergies
- Dextromethorphan – Cough suppressant
- Guaifenesin – Expectorant for chest congestion
- Pseudoephedrine – Nasal decongestant
- Phenylephrine – Nasal decongestant
- Omeprazole – Proton pump inhibitor for heartburn
- Lansoprazole – Proton pump inhibitor for heartburn
- Ranitidine – Antacid and H2 blocker for heartburn
- Calcium carbonate – Antacid for heartburn and indigestion
- Loperamide – Anti-diarrheal
- Bismuth subsalicylate – Anti-diarrheal and upset stomach relief
- Polyethylene glycol – Laxative for constipation
- Hydrocortisone cream – Anti-itch cream for rashes and skin irritation
How to use OTC drugs
Always carefully read the label for proper dosage, usage, and warnings.
Speak with a doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure about using a medication,
Keep medicines out of the reach of children and store them at cool & dry place.
FAQ
What are OTC drugs, and how are they different from prescription drugs?
OTC drugs are medications available without a prescription, used to treat common ailments like headaches, colds, and allergies. They differ from prescription drugs, which require a doctor’s authorization due to the need for specialized monitoring or treatment of more complex conditions.
Are OTC drugs safe to use without consulting a doctor?
Yes, OTC drugs are generally safe when used as directed on the label. However, it is essential to follow dosage instructions, be aware of potential side effects, and consult a healthcare professional if you have underlying health conditions or if symptoms persist.
Can I take multiple OTC drugs at the same time?
It is possible to take multiple OTC drugs simultaneously, but caution is needed to avoid overlapping active ingredients, which can lead to overdoses or adverse effects. Always check the labels for potential interactions and consult a pharmacist if unsure.
