Alpha-blockers are also recognized as α-adrenergic receptors antagonists. It is a class of medications that work by blocking the effects of norepinephrine and epinephrine on alpha-adrenergic receptors. Alpha blockers relax blood vessels, improve blood flow, that help to lowers high blood pressure and prostate issues. Alpha receptors are found in various parts of the body, mainly in the smooth muscles of blood vessels, the prostate, and the bladder.
They reduce blood pressure by expanding the cardiovascular system’s blood vessels. They make the bladder neck wider in the urinary tract to help urine flow better and get rid of any blockage that could be caused by an enlarged prostate or a kidney stone. Alpha blockers begin to work immediately, but the best results appear in four to six weeks of use.
What is the mechanism of action of Alpha blockers.
Alpha-blockers competitively inhibit the affinity of adrenaline & nor adrenaline to the alpha-adrenergic receptors. Adrenaline or nor adrenaline are released from adrenal glands, cause vasoconstriction and their inhibition lead to vasodilatation. There are two main subtypes of alpha-receptors:
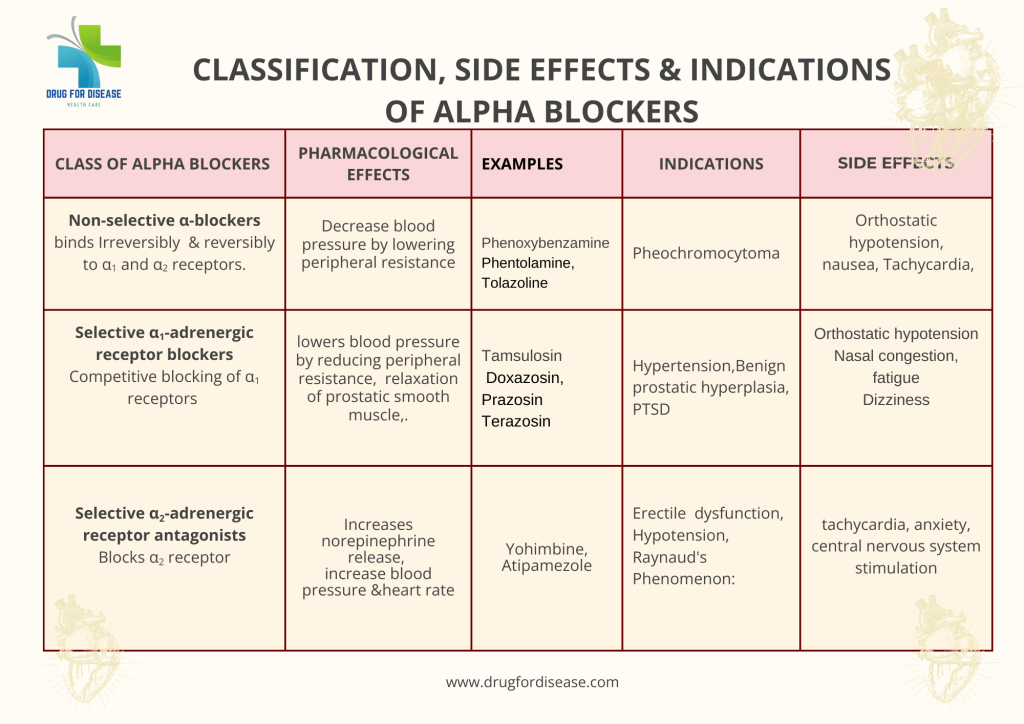
Non-Selective Alpha-Blockers: these drugs act on both alpha-(α1and α2) receptors and block their activity. Although these drugs are effective vasodilators, however less commonly indicated for hypertension treatment to side effects like reflex tachycardia and high sympathetic activity. They are mainly prescribed for specific conditions for a short time. Phenoxybenzamine and Phentolamine belongs to this group.
α1 receptors; These receptors are located throughout the body, mainly at the neck of bladder, smooth muscle cells in the walls of peripheral blood vessels & the prostate. Alpha-blockers widen the blood vessels and produce vasodilation by blocking these receptors. These drugs improve urine flow by the relaxation of the bladder neck and prostate. they are of three types named as α1A receptors, α1B receptors, α1D receptors. Prazosin, Terazosin, Doxazosin, Tamsulosin, Alfuzosin, Silodosin belongs to this group.
α2 receptors: These receptors are located on nerve terminals and other tissues.
Selective α1 receptors blocker are most commonly used alpha-blockers that minimize the side effects associated with the blocking of α2 receptors.
Indications
Alpha-blockers are mainly used to treat two main disorders
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Alpha-blockers are drug of choice for benign prostatic hyperplasia. BPH is due to the enlargement of the prostate gland with the symptoms like weak stream, frequent urination & dribbling. These drugs relax the smooth muscles, make the bladder neck wider in the urinary tract to help urine flow better and get rid of any blockage that could be caused by an enlarged prostate or a kidney stone.
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Although it is not the first choice or protocol, however in complex cases can be used along with other drugs. Alpha-blockers lower peripheral resistance by relaxing blood vessels that in turn lowers blood pressure.
Pheochromocytoma It is a rare disease of the adrenal gland having tumor, that secretes excessive amount of epinephrine and norepinephrine. Excessive release of catecholamines immensely raise blood pressure. Alpha-blockers are considered the first choice for managing hypertension in patients with pheochromocytoma, especially before surgery for the removal of tumor. alpha blockers block the effects of the excess hormones and prevent life-threatening hypertension during the surgical procedure.
Raynaud’s disease: It is a rare disease in which vasospasms occur mostly in the fingers and toes due to stress or cold. The drugs of this class can be used to reduce the frequency and severity of these vasospastic attacks by relaxing blood vessels.
Post traumatic stress disorder; Prazosin is utilized in the management of nightmares linked with Posttraumatic stress dsorder.
Alpha blockers can be used for purposes other than its intended use to help kidney stones pass. They can also help those who have trouble urinating by relaxing the smooth muscles of the bladder. Prazosin is utilized in the management of nightmares linked with PTSD and as an adjunctive treatment for pheochromocytoma. Dibenzyline is also used to help treat pheochromocytoma. Tamsulosin can help you pass kidney stones.
Side effects of alpha blockers
Orthostatic Hypotension: It is a condition in which a severe and sudden fall of blood pressure occurs, when a person stands up from a resting posture. It usually appears after first dose or when dose is increased. To minimize this effect and any injury of fall, it is better to take alpha blockers at night.
Nasal Congestion alpha blockers block α receptors present at nose, cause increased blood flow (vasodilatation) and nasal congestion or nasal stuffiness. it is a rare and minor side effect.
Sexual Dysfunction: This is a common and reversible side effect with drugs like tamsulosin and silodosin that are used for BPH. It is distressing for patients and need to discuss with a healthcare professional. Other side effects like edema, abnormal fluid retention may appear in the treatment of BPH.
Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome: this rare side effect may appear in people who are taking tamsulosin and at the same time undergoing cataract surgery. The iris of the eye becomes floppy and billows out during surgery. All alpha-blockers can cause IFIS, one must inform ophthalmologist before surgery.
Common side effects include dizziness, fatigue, palpitations and tachycardia
what are the Precautions
Liver and Kidney Disease. in case of renal & liver impairment dose must be reduced as per severity of impairment.
Cataract Surgery: All alpha-blockers can cause (Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome) IFIS, one must inform ophthalmologist before surgery.
Pregnancy or nursing; Most alpha blockers should be taken with caution during pregnancy because there isn’t enough human data to adequately assess the danger. The only drug in this class that has more benefits than hazards is phenoxybenzamine. There isn’t enough information on the risks to babies or the effects on milk production, therefore breastfeeding can be continued.
Children; Alpha blockers are applicable in pediatric patients for multiple diseases. Prazosin is utilized in the management of nightmares linked with PTSD and as an adjunctive treatment for pheochromocytoma. Dibenzyline is also used to help treat pheochromocytoma. Tamsulosin can help you pass kidney stones.
Older adults’ Alpha blockers are applicable for the elderly demographic. Orthostatic hypotension, risk of fall or injury due to orthostatic hypotension & frequent urination are the risk factors in the selection of alpha blockers. Their pharmacy team should collaborate with their cardiology and urology health care teams to make sure they can safely take alpha blockers.
Diuretics, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta blockers, and PDE-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction are more likely to be given to older persons.
Dosage Forms and Doses
Alpha-blockers are available in oral dosage forms either in the form of capsule or tablets. The dose depends on the specific drug, the medical condition, severity of disease and patient’s response. initial dose is low, increase gradually to manage medical conditions while minimizing side effects. some common alpha blockers along with bran names are as follow
Prazosin (Minipress): Tab. 1mg, 2mg, 5mg . mostly used for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and hypertension. initial dose is 1-2mg , in two or three doses & max dose is 20mg/day for high blood pressure.
Terazosin (Hytrin): Tab. 1mg, 5mg, indicated for the treatment of hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia. (BPH). initial dose 1 mg orally at bedtime. maximum dose is 20 mg/day.
Doxazosin (Cardura): Tab. 1mg, 4mg, indicated for the treatment of hypertension and benign prostatic hyperplasia. (BPH) Initial dose is 1 mg orally once a day & maximum dose 16 mg/day
Tamsulosin (Flomax): Starting dose 0.4 mg, once a day and gradually can be increased up to 0.8 mg if required., It should be given 30 minutes after a meal.
Alfuzosin (Uroxatral): Tab. 10mg mainly used for the treatment of BPH. The recommended dose is 10 mg once a day after meal.
Silodosin (Rapaflo): Tab 8mg, indicated for BPH & the recommended daily dose is 8mg with food.
Due to safety concerns and a higher risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes compared to other antihypertensive medications, alpha-blockers are typically not used as the first-line treatment for hypertension. However, when a patient has concurrent conditions that can be effectively treated with the same medication, they are the preferred option.