Hypertension (high blood pressure)
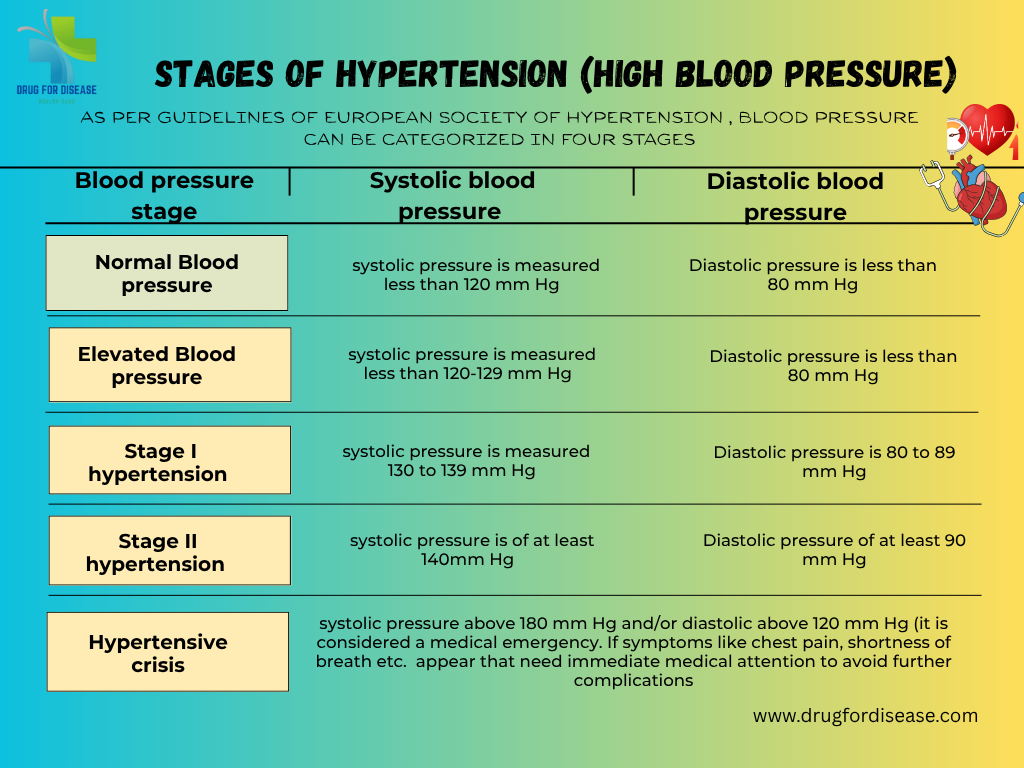
Hypertension or high blood pressure is the most common non communicable disease that appears when the force (pressure) of blood against the artery walls is continuously high. Or in other words consistent raised arterial pressure is termed as hypertension. How to take readings of hypertension Hypertension or high blood pressure is measured by two values that are systolic pressure & diastolic pressure. Systolic blood pressure represents the pressure of blood in arteries when heart beats & diastolic blood pressure is the pressure of blood is on artery walls when the heart muscle rests between beats. A normal blood pressure value is 120/80 mmHg. Hypertension or high blood pressure is usually diagnosed when blood pressure consistently exceeds 130/80 mmHg. Globally1.28 billion adults between the age of 30–79 years are suffering from hypertension. About two-thirds of hypertensive cases belong to low- and middle-income countries. It is the major cause of premature mortality (WHO, 16 March, 2023). Stages of Hypertension or high blood pressure As per European Society of hypertension guidelines, blood pressure can be categorized in four stages Normal Blood Pressure: systolic pressure is less than 120 mm Hg while diastolic is less than 80 mm Hg Elevated Blood pressure: systolic pressure of 120-129 mm Hg and diastolic less than 80 mm Hg, need to consult health care professional to manage the condition. Stage 1 Hypertension: systolic pressure of 130 to 139 mm Hg or diastolic of 80 to 89 mm Hg. It can be managed by lifestyle changes and medication. Stage 2 Hypertension: systolic pressure of at least 140 mm Hg or diastolic of at least 90 mm Hg or above. Hypertensive crisis: systolic pressure above 180 mm Hg and/or diastolic above 120 mm Hg (it is considered a medical emergency. Following symptoms may appear, that need immediate medical attention to avoid further complications chest pain, shortness of breath, difficulty in speaking, numbness, weakness, blurred vision etc. Types of Hypertensions (high blood pressure) Hypertension or high blood pressure is basically classified into two major types, that are Primary /Essential Hypertension; It is the most common type, affecting between 90 to 95 percent of people. It develops slowly over time and has no known cause, but linked to behavioral factors, genetic, environmental factors, diet, smoking, excessive salt intake, less physical activity etc Secondary Hypertension Secondary Hypertension or high blood pressure is affecting 5–10% percent of people worldwide. It occurs suddenly and is due to an underlying medical condition or conditions like adrenal gland tumors, thyroid problems, stroke, kidney failure, birth control tablets or medicines etc. Secondary hypertension is more prevalent in younger people & 30% of people have an age of 18 to 40 years. Other Subtypes of hypertension include Isolated Systolic Hypertension Mostly older people suffer with isolated systolic hypertension. Blood pressure ranges from 140- 90mmHg systolic pressure and diastolic pressure respectively. Malignant Hypertension (Hypertensive Emergency Blood pressure rises quickly and severely (typically >180/120 mmHg. It may cause damage to one or more organs like kidney, lungs, brain etc. symptoms.like confusion, anxiety, drowsiness, chest pain, and shortness of White Coat Hypertension: Elevated blood pressure only in clinical settings due to anxiety while patient gets normal at home Masked Hypertension; It is the vice versa of above readings is normal in clinical settings but elevated at home or in daily life. Gestational hypertension Hypertension occurs in approximately 8–10% of pregnancies after 20 weeks of gestation and women have a blood pressure higher than 140/90 at two readings with at least 6 hours gap Other pregnancy related hypertension or high blood pressure are Pre-eclampsia & Eclampsia that need special care and emergency treatment. Causes & Risk Factors of hypertension or high blood pressure No physical activity unhealthy diet that are rich in salt, sugar, saturated and trans fats, carbonated drinks, etc. smoking tobacco or being exposed to secondhand smoke that may damage blood arteries and cause high blood pressure. excessive salt intake anxiety or stress Being overweight or obese Family history or genetic factors Age and sex Adrenal tumors (e.g., pheochromocytoma) Medications (NSAIDs, steroids, birth control pills Chronic kidney disease Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism COMPLICATIONS OF HYPERTENSION Coronary heart disease (CHD) Myocardial infarction (MI) Stroke (CVA), either ischemic or intracerebral hemorrhage Hypertensive encephalopathy Renal failure, acute versus chronic Peripheral arterial disease Atrial fibrillation Pathophysiology & Diagnosis Increased salt absorption resulting in volume expansion Increased activation of the sympathetic nervous system An impaired response of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) It can be diagnosed by routine blood pressure monitoring with electronic or manual BP apparatus sphygmomanometer, blood tests (renal function, electrolytes, lipid profile), urine test etc. Treatment Plans Lifestyle Modifications Medications: Preferred drugs are Diuretics, Calcium channel blockersm ACE inhibitors, Beta blockers Identify and treat the underlying cause Adjust or stop contributing medications Hypertension or high blood pressure is often silent but deadly. Early detection, lifestyle changes, and appropriate treatment can prevent serious complications. Everyone over the age of 30 should monitor their blood pressure regularly—even if they feel healthy.
What Are Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)?
Non-communicable diseases are a group of medical conditions that are not transmitted from person to person. Rather, they come about due to the course of time and are often a result of poor eating habits, insufficient physical activities, use of tobacco, and the intake of alcohol in amounts that are beyond normal. These are the long-term health conditions that are driven by lifestyle or behavioural factors. A longitudinal study from 2003 to 2014 identified the spectrum and trends of non-communicable disease prevalence in inpatients of 12 hospitals in China. It is expected that by 2030, NCDs will be the main cause of death in Sub-Saharan Africa, killing more people than communicable, maternal, neonatal, and nutritional (CMNN) illnesses put together. Most common non-communicable diseases include: Cardiovascular disorders (17.9 million people died globally) Chronic respiratory diseases (9 million people died annually) Cancer (3.9 million people died annually) Diabetes (1.6 million people died annually) The above-mentioned have been responsible for about 70-80% of global morbidity & mortality, especially in the lower middle-income countries. NCDs not only burden the economy of a health system but also the quality of life of people. Cardiovascular diseases are the disorders of circulatory system, like High Blood Pressure, Peripheral Artery Disease, Rheumatic Heart Disease, stroke, etc. Chronic respiratory diseases are type of chronic diseases that appear due to the functional impairment of lungs and the respiratory system, like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, etc. Diabetes, a metabolic condition, occurs due to high blood sugar levels. mainly of three types: Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes & gestational diabetes. Cancer occurs due to the abnormal growth of cells that develop and spread without control. Some common cancer categories are lung cancer, breast cancer, colorectal cancer, etc. Risk factors of non-communicable diseases NCDs Behavioural risk factors Genetic risk factors Environmental risk factors Metabolic risk factors Socio-demographic factors Global Effects of NCD High Mortality Rate: According to the WHO report 2021, about 43 million people die every year due to noncommunicable diseases, and 82% of the mortality data is from lower-middle-income countries. Economic Burden: NCDs put a lot of stress and burden on healthcare systems and ultimately increase health costs. Higher Healthcare Costs: A lot of budget is required for the management of chronic conditions. These noncommunicable diseases need long-term medical care, drugs, improved healthcare systems like telehealth, & human resources to address these issues, all of which will add up to a lot of money. Lower Quality of Life or Reduced Work Capacity: People suffering with chronic diseases will be less productive towards work. It’s hard to do everyday things, causes discomfort, and may lead to disability. Policies for Public Health; To effectively manage common NCDs, it is important to put preventive health programs first and improve the healthcare system. Health education programs can give people in a community the information they need to avoid getting sick and find out about it early, which could lower the number of sick people. Tobacco Control: strong measures need to be adopted to control tobacco use, like increasing taxes, declaring smoke-free areas, and efforts to raise public awareness Promoting a Healthful Diet: Food having a high quantity of salt, sugar, and saturated and trans fats is linked to obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions. Labels on food items along with nutritional value & minimum price will be helpful. Promoting Physical Activity: need to build grounds, parks, paths to improve physical activity free of cost Alcohol Control: Implement rules to discourage drinking, like taxes, age limits on the purchase & sale of alcohol, and people awareness by social media. What healthcare actions need to be taken Improving air quality by developing and implementing policies of waste management, pollution, etc. Early detection and screening Management of risk factors especially behavioural factors Access to essential medicines and technology to every person Integrated Care Models Community-Based initiatives Self-Management Education In simple words, diseases that do not spread from person to person are a big threat to the health and well-being of people all over the world. The ratio of NCDs can be decreased and the health and quality of life of people enhanced by knowing what the risk factors are, using good prevention methods, and making sure everyone has access to appropriate healthcare centres. To properly deal with this worldwide problem, governments, healthcare professionals, communities, and individuals must all work together. FAQ 1. What are the most common non-communicable diseases? The most common non-communicable diseases include cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, chronic respiratory diseases, and cancer. These are lifestyle-related diseases, and this is commonly related to such aspects as diet, physical activities, and smoking. 2. How do non-communicable diseases impact a society? Non-communicable diseases place a significant burden on healthcare systems, economies, and individuals. These cause untimely deaths, disability and treatment that is very expensive, which are all related to the overall welfare of the society. 3. What are the risk factors that can be changed? Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) are significantly influenced by modifiable behavioural risk factors. that lifestyle changes, healthy diets, cessation of smoking & alcohol, improved physical activity, weight management, etc.
Smarter Local SEO: How Digital Marketing is Changing Small Businesses in Pakistan?
In today’s digital-first world, small businesses in Pakistan are discovering the transformative power of smarter local SEO. What was once limited to flyers, billboards, and word-of-mouth has now evolved into data-driven strategies, real-time engagement, and hyper-targeted visibility — all thanks to digital marketing. At DMT Lahore, we’ve seen firsthand how the right approach to local SEO can empower small businesses to compete, grow, and thrive, even in highly competitive markets like Lahore, Karachi, and Islamabad. In this article, we’ll explore how local SEO works, why it matters more than ever, and what strategies are helping Pakistani businesses win big online. What is Local SEO and Why Should Small Businesses Care? Local SEO (Search Engine Optimization) focuses on increasing the visibility of a business for location-based searches. Imagine someone in Lahore typing “best biryani near me” or “top real estate agents in DHA Lahore” — local SEO ensures that your business shows up at the right moment. For small businesses, this means: In short, it’s not just about getting found — it’s about getting found by the right people, right when they need you. How Digital Marketing Has Evolved Local SEO in Pakistan Over the past decade, digital marketing has completely redefined how small businesses engage with local audiences. Here’s how: Earlier, businesses focused on broad keywords like “shoe store Pakistan.” Today, smarter businesses target hyperlocal keywords like: This level of precision helps small businesses appear in front of customers who are most likely to visit or call. GMB is now the backbone of local SEO. Pakistani businesses that keep their GMB profiles updated — with photos, reviews, timings, and posts — enjoy higher visibility on Google Maps and local packs. At DMT Lahore, we advise clients to: More than 70% of local searches in Pakistan now come from smartphones. This shift has pushed businesses to: It’s all about reducing the gap between discovery and action. Blogs, videos, and social media posts tailored to local culture, events, and needs can dramatically boost engagement. For example: Localized content positions businesses as part of the community, not just a service provider. Why Small Businesses in Pakistan Must Act Now The digital landscape in Pakistan is evolving quickly. Internet penetration has crossed 40%, and with cheaper smartphones and better connectivity, more people are searching online than ever before. If your competitors are already investing in local SEO, waiting means falling behind. On the other hand, being early can help you dominate search results, build a loyal local audience, and get consistent leads without ongoing ad costs. Practical Local SEO Tips for Pakistani Businesses Here are actionable steps you can start today: Claim & Optimize Your GMB Listing Focus on Hyperlocal Keywords Use tools like Google Keyword Planner to find keywords that include your city, area, or even neighborhood. Collect Customer Reviews Happy customers are often willing to leave reviews if you ask politely. Reviews boost your local ranking and influence buying decisions. Build Local Backlinks Get featured on Pakistani business directories, local blogs, and community websites. Backlinks from local sources help search engines understand your relevance to your location. Create Location-Based Content How DMT Lahore Supports Small Businesses with Local SEO At DMT Lahore, we combine our local market understanding with global best practices to design local SEO strategies tailored for Pakistani businesses. Here’s what makes our approach effective: Our goal isn’t just to get you on the map — it’s to turn online visibility into real sales, calls, and walk-ins. The Future: AI, Voice Search, and Beyond As digital trends advance, local SEO is set to evolve further: Forward-thinking businesses that adapt quickly will keep leading the market. Smarter local SEO isn’t just an option anymore — it’s a necessity for small businesses in Pakistan. By embracing data-driven digital marketing, even modest businesses can reach local audiences more effectively, build trust, and grow sustainably. Whether you’re a cafe in DHA Lahore, a boutique in Liberty Market, or a real estate agent in Bahria Town, investing in local SEO today can set you apart for years to come. At DMT Lahore, we’re here to guide you every step of the way — from strategy to execution. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is indigestion?
Indigestion, or dyspepsia, is a common gastrointestinal illness that causes pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen that comes back often, usually after eating. It affects 20–40% of the population every year, and the symptoms might be modest and happen only sometimes, or they can be long-lasting and influence quality of life. It is normally not dangerous, but it can be a sign of a medical problem.Indigestion can be classified as organic indigestion & functional indigestion. Organic indigestion is due to some underlying disease like gastritis, ulcer, etc., while functional is without evidence of underlying disease. What are the causes of indigestion Occasional indigestion is simple, and many people suffer after having a meal. However, the one that lasts longer is often less simple. There are many different reasons for indigestion, which can be grouped into the following: Behavioural and Dietary Trigger Foods that are fatty, spicy, or acidic; excessive coffee; high alcohol consumption; carbonated drinks; chocolate; etc. Medicines: NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen and aspirin). Antibiotics (macrolides & metronidazole), bronchodilators, anti-diabetic drugs (metformin), cardiovascular drugs (ACE inhibitors), cholesterol-reducing agents, neuropsychiatric medications, corticosteroids, iron, etc. Lifestyle: Overeating, eating too quickly, eating late at night, smoking, and being stressed or anxious Causes of Organic dyspepsia Acid reflux, or GERD (when stomach acid flows back into the oesophagus) Peptic ulcers are lesions in the stomach or duodenum that are typically caused by H. pylori infection. Gastritis (inflammation of the stomach lining) or gastroparesis (delayed emptying of the stomach) Pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer, Gallbladder inflammation Functional Dyspepsia No underlying cause (60% of cases). Related to visceral hypersensitivity, problems with the gut-brain axis can cause changes in gut motility Being pregnant, hormonal changes and pressure from the uterus on the stomach can produce temporary indigestion, especially after 27 weeks Demographics: Women are more affected, as are people of ages above 55-60 years. Symptoms Symptoms usually start after eating and can last from a few minutes to a few hours Pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen, like burning. Early satiety is not being able to finish a meal. Postprandial fullness: feeling full for a long time after eating Feeling bloated, burping, sick to your stomach, and throwing up; heartburn (a burning feeling in the chest) or acid reflux; loud gurgling in the stomach; Symptoms that are red flags and need immediate care Difficulty in swallowing (trouble eating), losing weight for no reason, or having anaemia. Haematemesis is when you vomit blood, and melena is when your faeces are black. Severe discomfort or pain in the chest, like a heart attack. Plan for Treatment; Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications: Antacids for quick relief remain effective for a short duration. H2 blockers, like famotidine, lower the amount of acid that the stomach makes. The effects continue for hours. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs), such as omeprazole: Strong acid suppression; used for 2 to 4 weeks. Treatments that are prescribed The “test and treat” approach (using a urea breath test or faecal antigen test) is considered the most effective and widely recommended protocol. Antibiotics: For sure H. pylori (such amoxicillin and clarithromycin) along with PPI Prokinetics, like metoclopramide, speed up the emptying of the stomach by improving the motility of the GIT system. Other treatments Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) or stress management for functional dyspepsia can help with mental health. Herbal teas like peppermint and ginger can help with digestion. Drinking water in little quantity or with sips will help a little How to prevent Improve eating habits by taking five to six little meals a day & chewing well. Don’t eat 3–4 hours before bed. Modify lifestyle by weight management, regular exercise, and use of healthy diets. When to Get Medical Help If you have any of the following, see a doctor for medical advice Symptoms last more than two weeks even with over-the-counter medication. Symptoms that are red flags start to show up (such as weight loss and dysphagia, i.e., difficulty swallowing). Shortness of breathe or tightness of chest Persistent vomiting, vomiting with blood or black stools, and unintentional weight loss. Patients with a known history of peptic ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding may need testing to check for recurrence or complications. Diagnosis requires tests like H. pylori breath/stool tests, endoscopy, or blood tests. Conclusion Indigestion can be managed with adjustments to your food and lifestyle and over-the-counter medicines. But if the disease is chronic or severe, you must consult a doctor. Long-term control depends on preventive measures that focus on avoiding triggers, eating mindfully, and lowering stress. FAQ What is indigestion & its causes? indigestion is the discomfort of upper abdomen and is mostly due to spicy food, stress, or some underlying diseases like H. pylori infection, gastritis, or GERD, etc. What are the common symptoms of indigestion? Common symptoms include bloating, heartburn, satiety (feeling of fullness), nausea, vomiting, and burping. How can indigestion be diagnosed? Diagnosis is usually based on symptoms. Tests like the H. pylori breath test, stool tests, or endoscopy may be performed according to patient conditions and ACG/CAG dyspepsia guidelines. If patient age is ≥60 years, an upper GI endoscopy needs to be prescribed. What will be treatment options for indigestion? Treatment may include lifestyle and dietary modifications and stress reduction. immediate and quick relief by over-the-counter drugs, like antacids & proton pump inhibitors (PPIs); however, if symptoms persist or worsen, you need to consult a doctor immediately. How to prevent indigestion? Lifestyle and dietary modifications, eating small and chewing well, managing stress, weight reduction, and improving physical activity will help to prevent it.

