Non-communicable diseases are a group of medical conditions that are not transmitted from person to person. Rather, they come about due to the course of time and are often a result of poor eating habits, insufficient physical activities, use of tobacco, and the intake of alcohol in amounts that are beyond normal. These are the long-term health conditions that are driven by lifestyle or behavioural factors. A longitudinal study from 2003 to 2014 identified the spectrum and trends of non-communicable disease prevalence in inpatients of 12 hospitals in China. It is expected that by 2030, NCDs will be the main cause of death in Sub-Saharan Africa, killing more people than communicable, maternal, neonatal, and nutritional (CMNN) illnesses put together.
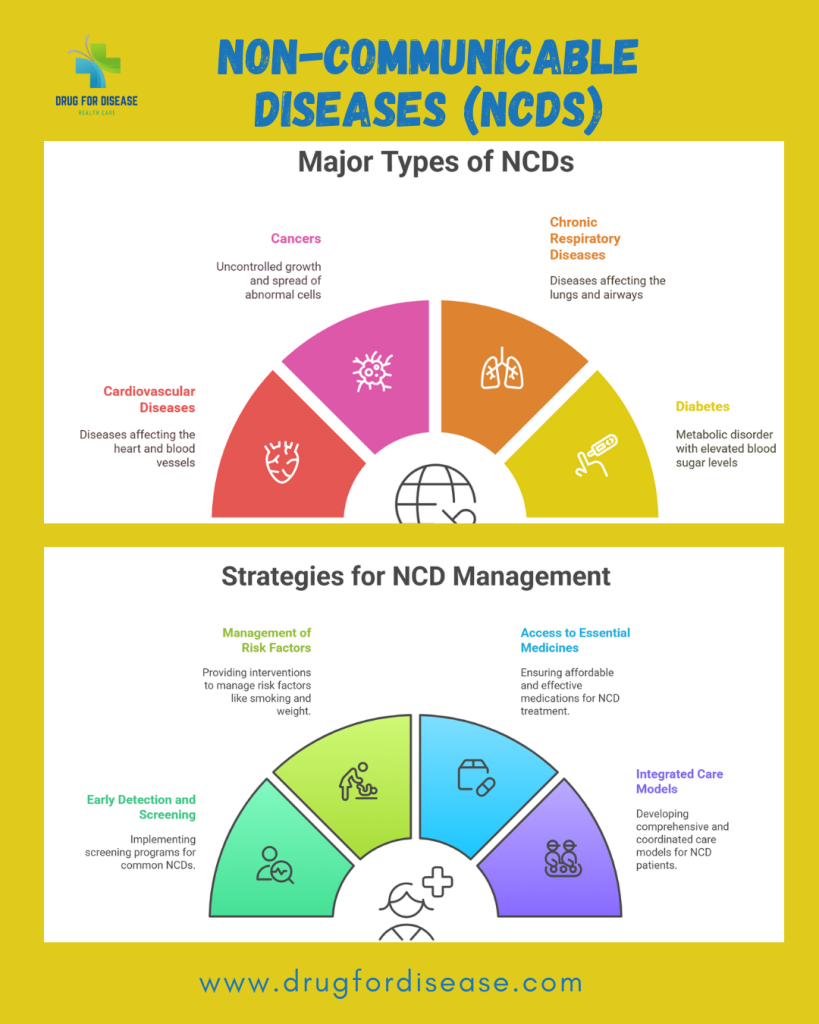
Most common non-communicable diseases include:
Cardiovascular disorders (17.9 million people died globally)
Chronic respiratory diseases (9 million people died annually)
Cancer (3.9 million people died annually)
Diabetes (1.6 million people died annually)
The above-mentioned have been responsible for about 70-80% of global morbidity & mortality, especially in the lower middle-income countries. NCDs not only burden the economy of a health system but also the quality of life of people.
Cardiovascular diseases are the disorders of circulatory system, like High Blood Pressure, Peripheral Artery Disease, Rheumatic Heart Disease, stroke, etc.
Chronic respiratory diseases are type of chronic diseases that appear due to the functional impairment of lungs and the respiratory system, like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, etc.
Diabetes, a metabolic condition, occurs due to high blood sugar levels. mainly of three types: Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes & gestational diabetes.
Cancer occurs due to the abnormal growth of cells that develop and spread without control. Some common cancer categories are lung cancer, breast cancer, colorectal cancer, etc.
Risk factors of non-communicable diseases NCDs
Behavioural risk factors
Genetic risk factors
Environmental risk factors
Metabolic risk factors
Socio-demographic factors
Global Effects of NCD
High Mortality Rate: According to the WHO report 2021, about 43 million people die every year due to noncommunicable diseases, and 82% of the mortality data is from lower-middle-income countries.
Economic Burden: NCDs put a lot of stress and burden on healthcare systems and ultimately increase health costs.
Higher Healthcare Costs: A lot of budget is required for the management of chronic conditions. These noncommunicable diseases need long-term medical care, drugs, improved healthcare systems like telehealth, & human resources to address these issues, all of which will add up to a lot of money.
Lower Quality of Life or Reduced Work Capacity: People suffering with chronic diseases will be less productive towards work. It’s hard to do everyday things, causes discomfort, and may lead to disability.
Policies for Public Health;
To effectively manage common NCDs, it is important to put preventive health programs first and improve the healthcare system. Health education programs can give people in a community the information they need to avoid getting sick and find out about it early, which could lower the number of sick people.
Tobacco Control: strong measures need to be adopted to control tobacco use, like increasing taxes, declaring smoke-free areas, and efforts to raise public awareness
Promoting a Healthful Diet: Food having a high quantity of salt, sugar, and saturated and trans fats is linked to obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions. Labels on food items along with nutritional value & minimum price will be helpful.
Promoting Physical Activity: need to build grounds, parks, paths to improve physical activity free of cost
Alcohol Control: Implement rules to discourage drinking, like taxes, age limits on the purchase & sale of alcohol, and people awareness by social media.
What healthcare actions need to be taken
Improving air quality by developing and implementing policies of waste management, pollution, etc.
Early detection and screening
Management of risk factors especially behavioural factors
Access to essential medicines and technology to every person
Integrated Care Models
Community-Based initiatives
Self-Management Education
In simple words, diseases that do not spread from person to person are a big threat to the health and well-being of people all over the world. The ratio of NCDs can be decreased and the health and quality of life of people enhanced by knowing what the risk factors are, using good prevention methods, and making sure everyone has access to appropriate healthcare centres. To properly deal with this worldwide problem, governments, healthcare professionals, communities, and individuals must all work together.
FAQ
1. What are the most common non-communicable diseases?
The most common non-communicable diseases include cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, chronic respiratory diseases, and cancer. These are lifestyle-related diseases, and this is commonly related to such aspects as diet, physical activities, and smoking.
2. How do non-communicable diseases impact a society?
Non-communicable diseases place a significant burden on healthcare systems, economies, and individuals. These cause untimely deaths, disability and treatment that is very expensive, which are all related to the overall welfare of the society.
3. What are the risk factors that can be changed?
Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) are significantly influenced by modifiable behavioural risk factors. that lifestyle changes, healthy diets, cessation of smoking & alcohol, improved physical activity, weight management, etc.